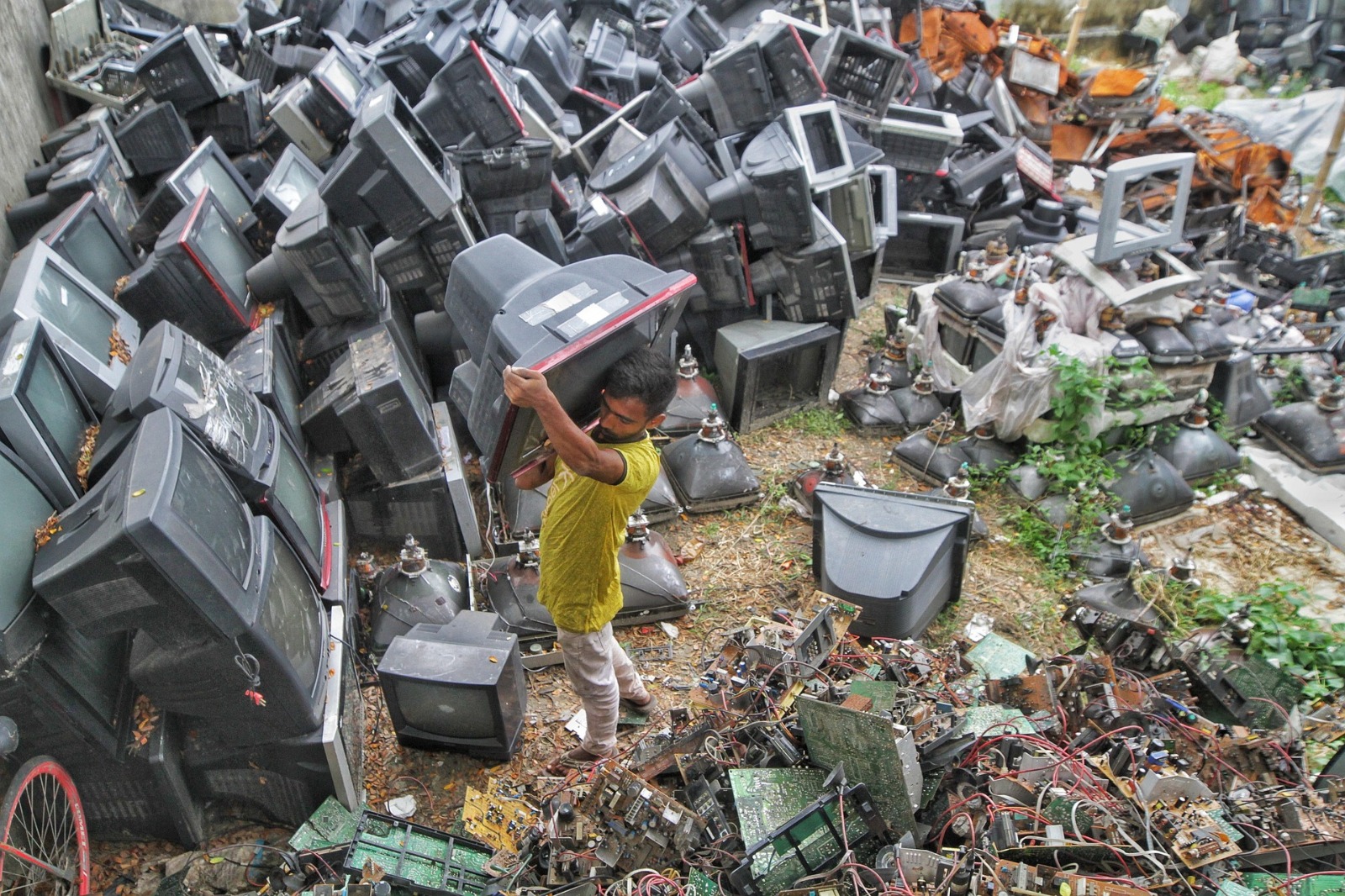

Electronic waste, or e-waste for short, is what we call all those old electrical and electronic gadgets we don't want anymore - things like smartphones, computers, TVs, and even batteries. Because we're always after the latest tech gadgets, and since technology keeps changing so fast, we're seeing way more e-waste piling up around the world than ever before. As we use more and more digital stuff in our lives, dealing with the environmental and health problems caused by e-waste is becoming super important.
Experts think that the amount of e-waste we're generating globally is reaching scary levels, estimating it topped 52 million metric tons in 2021. All this extra waste is a big problem because e-waste often has a bunch of dangerous materials that, if not handled correctly, can really hurt both our planet and our health.
Think of e-waste as a massive junk pile of old electronics. We're talking about everything from your old phone and laptop to that outdated TV and even used batteries. What's inside these devices? It's a real mix! You'll find metals, plastics, and ceramics, and some of these are pretty nasty, like toxic chemicals. Modern gadgets can have up to 60 different elements in them. This makes them a treasure trove for valuable metals that can be reused, but it also means they're a big threat to our environment and health if not handled properly.
Okay, here's a more human-like paraphrase of the text, keeping the same meaning and language:
Our old electronics are packed with nasties like lead, mercury, cadmium, and those pesky brominated flame retardants. If we don't get rid of them the right way, these chemicals can seep into the ground, contaminate our water, and pollute the air, causing some serious damage to our planet.
When we throw away our electronics improperly – like tossing them in landfills or burning them – they let off toxic fumes and leak harmful substances. This is especially bad in developing countries, where a lot of the world's e-waste ends up, leading to really bad soil and water pollution because of unsafe disposal practices.
Making, shipping, and getting rid of our electronic devices uses up a ton of energy and creates a lot of carbon emissions. raw materials and cranking out all those new gadgets uses a massive amount of power, leaving behind a pretty big carbon footprint.
Guiyu, known for having the world's biggest e-waste dump, suffers from very bad water pollution and high amounts of toxic chemicals in the air. Agbogbloshie, Ghana: This place is one of the largest e-waste processing areas, and workers there are being exposed to dangerous levels of toxic metals because of unsafe recycling methods.
Recycling electronic waste, or "e-waste," involves several steps: gathering old devices, taking them apart, reclaiming usable materials, and getting rid of any dangerous parts in a safe way. When done right, recycling lets us get back valuable stuff like gold, silver, and copper, while also making sure harmful chemicals are dealt with properly.
E-Stewards Certification: This label promises that e-waste is being recycled in a fair and eco-friendly manner.
R2 Certification: This focuses on smart ways to reuse and recycle electronics.
In places like the USA, the EU, and Japan, governments have rules and special programs to help people return old electronics, which promotes better e-waste management.
Instead of tossing your old devices in the trash, consider giving them to charity or selling them online. Websites like eBay and Facebook Marketplace, or even stores that specialize in refurbished tech, are great places to find a new home for your old electronics.
Many tech companies have programs that let you send back your old devices for proper recycling. Big names like Apple, Samsung, and Dell all have initiatives in place to help cut down on e-waste.
Consider buying refurbished electronics rather than brand-new ones. Also, support companies that use sustainable materials and make products in an energy-efficient way. Look for products built to last and with modular parts, which makes them easier to fix and upgrade.
E-waste represents an escalating environmental crisis that demands immediate action. The improper disposal of electronic devices results in pollution, health risks, and wasted resources. By educating ourselves about e-waste, recycling responsibly, and making sustainable choices, we can lessen its impact on our planet.
As consumers, we hold the power to effect change. Raise awareness, recycle responsibly, and back sustainable technology. The future of our environment hinges on the decisions we make today.